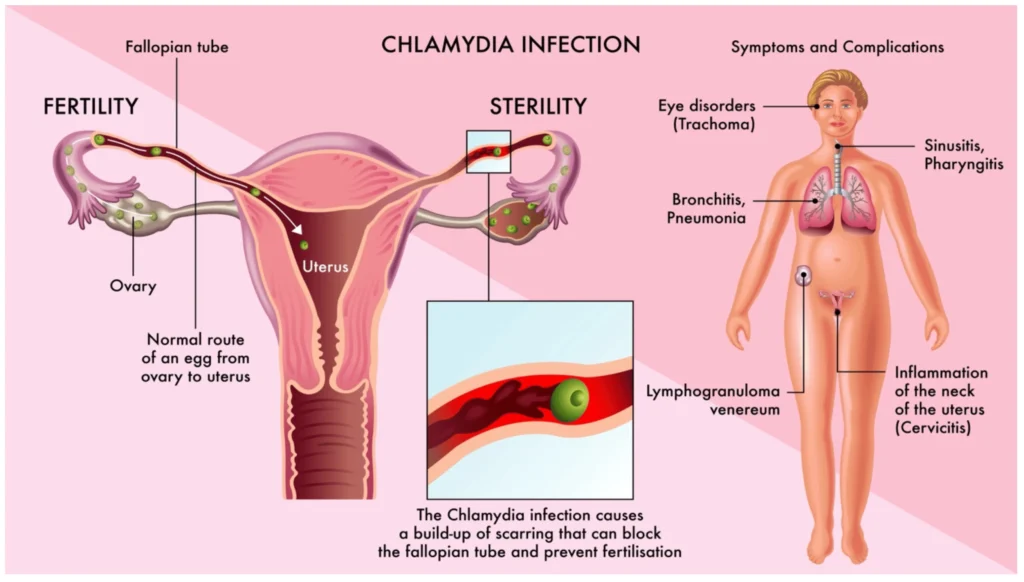
Chlamydia Risk Factors
Chlamydia, a sexually transmitted infection (STI), is a common health concern worldwide. In this article, we will delve into the multiple risk factors associated with the transmission and infection of Chlamydia. Understanding these risk factors is essential in promoting prevention strategies, raising awareness, and encouraging safe sexual practices.
Sexual Activity
Engaging in unprotected sex, having multiple sexual partners, or having sex at a young age can increase the risk of acquiring Chlamydia.
Unprotected sex refers to having sexual intercourse without using any form of barrier method, such as condoms or dental dams. This lack of protection increases the chances of Chlamydia transmission, as the bacteria can easily be passed between partners through bodily fluids.
Having multiple sexual partners also increases the risk of Chlamydia, as each new partner introduces the potential for exposure to the infection. The more sexual partners an individual has, the higher their risk becomes.
engaging in sexual activity at a young age can increase the risk of acquiring Chlamydia. Teenagers and young adults may have limited knowledge about safe sex practices and may be less likely to use protection consistently. Lack of awareness, inexperience, and peer pressure can all contribute to higher rates of Chlamydia among this age group.
To further illustrate the impact of sexual activity on Chlamydia risk, here is a breakdown of the factors:
- Engaging in unprotected sex: Increases chances of transmission due to direct exposure to bodily fluids.
- Having multiple sexual partners: Increases exposure to different individuals and potential carriers of Chlamydia.
- Having sex at a young age: Limited knowledge, inexperience, and decreased use of protection contribute to higher risk.
It is important for individuals to be aware of the risks associated with sexual activity and take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their partners. Using barrier methods consistently and correctly, getting regular STI screenings, and practicing open and honest communication with sexual partners can all help reduce the risk of acquiring Chlamydia.
Age and Gender
When it comes to Chlamydia infection, certain age groups and genders are more susceptible than others. Young adults and women, in particular, face a higher risk of acquiring Chlamydia. Let’s explore why this is the case.
Young Adults:
One of the main reasons young adults are more susceptible to Chlamydia is due to a lack of awareness and experience. Teenagers and young adults may not have received comprehensive sexual education, leaving them less informed about safe sexual practices. This lack of knowledge can contribute to higher rates of Chlamydia transmission.
young adults tend to have higher levels of sexual activity compared to other age groups. With increased sexual activity comes an increased likelihood of coming into contact with Chlamydia. Therefore, the combination of a lack of sexual education and higher sexual activity levels makes young adults more susceptible to Chlamydia infection.
Women:
Women, especially those under the age of 25, are at a higher risk of Chlamydia infection due to both physiological factors and potential asymptomatic cases. The anatomy of the female reproductive system makes it easier for Chlamydia bacteria to establish an infection.
Furthermore, Chlamydia can often be asymptomatic in women, meaning they may not experience any noticeable symptoms. This can lead to undiagnosed and untreated infections, increasing the risk of long-term complications. Regular screening and testing are crucial for sexually active women, particularly those in high-risk age groups, to detect Chlamydia early and prevent further spread.
certain age groups, namely young adults, and women are more susceptible to Chlamydia infection due to a combination of factors such as lack of sexual education, increased sexual activity, and physiological differences. Recognizing these risk factors is vital in promoting prevention strategies, raising awareness, and ensuring individuals have access to necessary healthcare and sexual education.
Adolescents and Young Adults
Adolescents and young adults are at a higher risk of acquiring Chlamydia due to a lack of awareness and experience. This age group often lacks proper sexual education, resulting in a limited understanding of safe sexual practices. Without this knowledge, they may engage in risky behaviors that can lead to Chlamydia transmission.
Furthermore, teenagers and young adults often have a higher level of sexual activity compared to other age groups. This increased sexual activity can increase their likelihood of coming into contact with Chlamydia and subsequently becoming infected.
The lack of experience among adolescents and young adults also contributes to a higher risk of Chlamydia. With limited sexual experience, they may be less likely to recognize the symptoms of Chlamydia or seek medical treatment promptly. As a result, the infection can go unnoticed and untreated for a longer period, leading to potential complications.
It is important to note that this age group may face additional challenges when it comes to accessing healthcare and sexual education. There may be barriers such as stigma, confidentiality concerns, or lack of resources that prevent them from seeking information or getting tested for Chlamydia.
Education and prevention efforts should specifically target adolescents and young adults to address these risk factors. By providing comprehensive sexual education, promoting safe sexual practices, and increasing awareness about Chlamydia, we can reduce the prevalence of this infection among this vulnerable population.
Lack of Sexual Education
One of the significant risk factors contributing to a higher Chlamydia risk among young adults is the lack of sexual education. Insufficient knowledge and understanding of safe sexual practices can leave young adults vulnerable to Chlamydia infection.
Without proper sexual education, individuals may not fully understand the importance of using barrier methods such as condoms to prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like Chlamydia. They may not be aware of the need for regular testing or the signs and symptoms of Chlamydia infection.
This lack of knowledge can lead to riskier sexual behavior and an increased likelihood of engaging in unprotected sex. Young adults may underestimate the risks or fail to recognize the importance of practicing safe sex, putting themselves at higher risk for Chlamydia.
Effective sexual education plays a critical role in empowering young adults with the necessary information and skills to make informed decisions about their sexual health. It can provide comprehensive information about STIs, including Chlamydia, and educate young adults about methods of prevention.
Sexual education programs can address topics such as the proper use of condoms, the importance of regular STI testing, and the consequences of engaging in risky sexual behavior. They can also provide information on where to access healthcare resources and STI testing services.
By improving sexual education among young adults, we can help reduce the rates of Chlamydia transmission and infection. Providing accurate information, dispelling myths, and promoting healthy sexual practices can empower young adults to prioritize their sexual health and make informed choices that contribute to their overall well-being.
It is essential for educational institutions, healthcare providers, and communities to work together to ensure that comprehensive sexual education is accessible to all young adults. By doing so, we can increase awareness, promote safer sexual practices, and ultimately reduce the risk of Chlamydia and other STIs among this vulnerable population.
Increased Sexual Activity
Increased Sexual Activity leads to a higher likelihood of Chlamydia transmission, especially among young adults who engage in higher levels of sexual activity. In these younger age groups, there is often a sense of exploration and experimentation, which can result in more sexual encounters and increased chances of exposure to Chlamydia.
The desire for intimacy and sexual experiences is natural and can be an exciting part of one’s life. However, it is important to be aware of the potential risks involved, including the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as Chlamydia.
When individuals engage in sexual activity without proper protection, such as using condoms or barrier methods, they are putting themselves at a higher risk of contracting Chlamydia. This is because Chlamydia is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, or oral intercours
Young adults who have multiple sexual partners are more likely to be exposed to Chlamydia. Each sexual encounter with an infected partner increases the risk of transmission. It is important to remember that Chlamydia can be asymptomatic, meaning people may not experience any symptoms even if they are infected, further increasing the possibility of spreading the infection unknowingly.
It is vital for individuals engaging in increased sexual activity to prioritize their sexual health and take necessary precautions. This might include practicing safe sex by consistently and correctly using condoms, getting regular STI testing, and discussing sexual health with their partners.
Education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting safer sexual practices. By providing comprehensive sexual education, individuals can gain a better understanding of the potential risks associated with increased sexual activity and learn how to protect themselves and their partners.
- Choose to have open and honest conversations with sexual partners about sexual health and STIs.
- Seek regular medical check-ups and screenings to detect and treat any potential infections.
- Be aware of the signs and symptoms of Chlamydia, such as abnormal discharge, pain during urination, or pelvic pain, and seek medical attention if necessary.
Remember, engaging in sexual activity is a personal choice, but it is essential to make informed decisions and take necessary precautions to reduce the risk of Chlamydia transmission and protect one’s sexual health.
Women
Women, especially those under 25 years old, have a higher susceptibility to Chlamydia infection compared to other age groups. This increased risk is influenced by several factors, including physiological factors and the potential for asymptomatic cases.
Physiological factors play a significant role in the higher vulnerability of young women to Chlamydia infection. The cervix in young women is not fully matured, making it more susceptible to the bacteria that cause Chlamydia. the cervix has more glandular cells that are targeted by the infection, further increasing the chances of acquiring Chlamydia.
Another important consideration is the potential for asymptomatic cases in women. Chlamydia infection can often go unnoticed as it may not present with any noticeable symptoms. This is particularly true for women, as they are more likely to have asymptomatic infections, making it difficult to detect and treat the infection in its early stages.
Due to the lack of symptoms, women may unknowingly harbor the infection for an extended period, increasing the risk of complications, such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can lead to long-term reproductive health issues, including infertility, if left untreated.
It is crucial for young women to prioritize regular screenings for Chlamydia, especially if they are sexually active or engage in risky sexual behavior. Early detection and prompt treatment can prevent the spread of the infection and reduce the risk of complications.
Furthermore, raising awareness among women about the importance of safe sexual practices and regular testing is essential in preventing the transmission of Chlamydia. Educating women about the potential risks and the availability of healthcare resources can empower them to take proactive measures to protect their sexual health.
women, particularly those under 25 years old, are more susceptible to Chlamydia infection due to physiological factors and the potential for asymptomatic cases. By addressing these risk factors and promoting proactive measures such as regular screenings, we can effectively prevent the spread of Chlamydia and protect women from the potential complications associated with the infection.
Unprotected Sexual Practices
Unprotected sexual practices significantly increase the risk of Chlamydia transmission. This includes engaging in vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse without using barrier methods such as condoms or dental dams. By not using these protective measures, individuals are exposing themselves to a higher likelihood of contracting Chlamydia.
Condoms, for example, act as a physical barrier between sexual partners, preventing the exchange of bodily fluids and reducing the risk of Chlamydia transmission. When condoms are not used consistently or correctly, the chances of contracting the infection increase.
It is important to note that Chlamydia can be transmitted through any type of sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse. Many people may underestimate the risk of transmitting or acquiring Chlamydia through oral sex, but it is important to practice safe oral sex as well. Using dental dams or condoms to cover the mouth and genitals during oral sex can help prevent transmission.
In addition to barrier methods, practicing open communication with sexual partners about their sexual history and getting tested regularly for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) is crucial. This allows for early detection and treatment if necessary, reducing the risk of Chlamydia transmission.
Engaging in unprotected sexual practices not only puts individuals at risk for Chlamydia but also increases the risk of acquiring other STIs. The use of condoms and other barrier methods not only reduces the risk of Chlamydia transmission but also protects against other infections such as gonorrhea, HIV, and herpes.
Engaging in unprotected sex without using barrier methods like condoms significantly increases the risk of Chlamydia transmission. It is important to prioritize safe sexual practices, including consistent and correct use of condoms, dental dams, and open communication with sexual partners. Taking these precautions can help reduce the risk of Chlamydia infection and promote overall sexual health.
Failure to Use Barrier Methods
Not using condoms consistently and correctly during sexual intercourse can lead to higher chances of Chlamydia transmission.
Why is using a barrier method important?
- Condoms act as a physical barrier, preventing the exchange of bodily fluids between sexual partners.
- They help to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections, including Chlamydia.
- When used correctly and consistently, condoms have been proven to be highly effective in preventing the transmission of Chlamydia and other sexually transmitted infections.
- Condoms are easily accessible and affordable, making them an essential tool for practicing safe sex.
How does the failure to use barrier methods contribute to Chlamydia transmission?
When individuals engage in sexual activity without the use of barrier methods, such as condoms, they expose themselves to a higher risk of Chlamydia transmission. This applies to all types of sexual intercourse, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex.
Chlamydia can be easily transmitted through the exchange of infected bodily fluids, such as semen or vaginal secretions. Without the protection of a barrier, the Chlamydia bacteria can easily pass from one partner to the other, leading to infection.
It’s important to note that Chlamydia can be present in individuals who do not show any symptoms. This means that even if someone appears to be healthy and free of any signs of infection, they may still be carriers of the bacteria. Using a barrier method, like a condom, helps to reduce the risk of transmission, regardless of whether or not symptoms are present.
How can individuals increase their adherence to barrier methods?
Improving adherence to barrier methods is crucial in preventing Chlamydia transmission. Here are a few tips to increase compliance:
- Education and awareness: Learning about the importance of barrier methods and their effectiveness in preventing Chlamydia can motivate individuals to use them consistently.
- Communication and consent: Openly discussing sexual health with partners and ensuring mutual consent to use barrier methods can help create a supportive and responsible sexual environment.
- Accessibility: Making condoms easily accessible, either through purchasing or obtaining them from clinics or healthcare providers, can remove barriers to consistent use.
- Proper usage education: Providing information on how to correctly use condoms, including correct storage, application, and disposal, can help individuals feel more confident in their usage.
By addressing the failure to use barrier methods and promoting their consistent and correct usage, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of Chlamydia transmission and protect their sexual health.
Concurrent Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Having other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) concurrently, such as gonorrhea or HIV, significantly increases the risk of Chlamydia infection. When someone is already infected with another STI, their immune system may be compromised, making them more susceptible to contracting additional infections, including Chlamydia.
One reason for this increased risk is the potential for co-infection. When someone has an existing STI, their body may already be weakened or have inflamed and damaged tissue, providing an ideal environment for other infections, like Chlamydia, to take hold. certain STIs can cause ulcers or lesions in the genital area, which can make it easier for Chlamydia to enter the body.
The presence of other STIs can also increase the likelihood of engaging in higher-risk sexual behaviors. When individuals have multiple concurrent STIs, they may be more likely to have sex with partners who also have infections, leading to a higher risk of Chlamydia transmission. This is particularly true for individuals who engage in unprotected sex or have multiple sexual partners.
It is important to note that some STIs, such as gonorrhea or HIV, can weaken the immune system and make the body more susceptible to various infections, including Chlamydia. The immune system plays a critical role in fighting off infections, so when it is compromised, the chances of contracting additional infections increase.
Preventing and treating other STIs is crucial in reducing the risk of Chlamydia infection. Regular testing for STIs and seeking immediate treatment if positive is essential. It is also important to practice safe sex by using barrier methods, such as condoms, to reduce the likelihood of transmitting or acquiring any STI, including Chlamydia.
Concurrent STIs, such as gonorrhea or HIV, significantly increase the risk of Chlamydia infection. The presence of other infections weakens the immune system and can lead to higher-risk sexual behaviors, increasing the chances of transmission. Taking steps to prevent and treat STIs is vital in reducing the likelihood of Chlamydia infection and protecting overall sexual health.

Personal and Social Factors
=Certain personal and social behaviors can increase the risk of Chlamydia transmission and infection.
When it comes to Chlamydia risk factors, personal and social behaviors play a significant role. These factors can contribute to the spread and infection of Chlamydia, a sexually transmitted infection that affects millions of people worldwide. It is essential to understand these factors to adopt preventive strategies and promote safe sexual practices.
One personal factor that increases the risk of Chlamydia transmission is substance abuse. Engaging in alcohol or drug abuse can lead to riskier sexual behaviors, such as unprotected intercourse or having multiple partners. Substance abuse may impair judgment and decision-making abilities, making individuals more prone to engaging in high-risk sexual activities that can facilitate Chlamydia transmission.
Another personal and social factor that can contribute to the risk of Chlamydia infection is low socioeconomic status. Individuals with limited financial resources may have restricted access to healthcare and sexual education. The lack of proper healthcare facilities and knowledge about safe sexual practices increases the likelihood of Chlamydia transmission. It is crucial to address the socioeconomic disparities and ensure that everyone has access to comprehensive sexual education and affordable healthcare services.
Understanding and addressing personal and social factors that increase Chlamydia risk is vital in preventing the spread of this infection. By promoting awareness, providing comprehensive sexual education, and ensuring access to healthcare services, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of Chlamydia and promoting overall sexual health and well-being.
Substance Abuse
Engaging in substance abuse, such as alcohol or drugs, may lead to riskier sexual behaviors, increasing the chances of acquiring Chlamydia.
Substance abuse is a major risk factor for Chlamydia transmission and infection. When individuals engage in alcohol or drug abuse, their judgment and decision-making abilities become impaired, leading to riskier sexual behaviors. This includes engaging in unprotected sex, having multiple sexual partners, and engaging in high-risk sexual activities.
Alcohol, for example, is a substance that can lower inhibitions and impair judgment. When under the influence, individuals may be more likely to engage in sexual activities without using barrier methods like condoms, putting themselves at a higher risk of Chlamydia transmission. Similarly, drug use, such as cocaine or methamphetamine, can increase sexual desire and lead to prolonged and risky sexual encounters, further increasing the chances of acquiring Chlamydia.
It is important to note that substance abuse not only affects the individual engaging in the risky behaviors but also their sexual partners. If one partner is under the influence of alcohol or drugs, they may not prioritize or prioritize incorrectly engaging in safe sexual practices. This puts both parties at risk of Chlamydia infection and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Addressing substance abuse is crucial in promoting Chlamydia prevention and reducing transmission rates. Encouraging individuals to seek help for their substance abuse issues can lead to healthier decision-making regarding their sexual activities and reduce their vulnerable position for acquiring Chlamydia.
Comprehensive sexual education programs should also include information on the relationship between substance abuse and risky sexual behaviors. By providing individuals with a clear understanding of the negative consequences of substance abuse on their sexual health, they can make informed choices to protect themselves and reduce their chances of acquiring Chlamydia.
Engaging in substance abuse, such as alcohol or drugs, can significantly increase the chances of acquiring Chlamydia. It impairs judgment, leading to riskier sexual behaviors and a higher likelihood of transmission. Addressing substance abuse and providing comprehensive sexual education are essential steps in reducing Chlamydia transmission rates and promoting healthier sexual practices.
Low Socioeconomic Status
Individuals with low socioeconomic status face unique challenges when it comes to Chlamydia prevention and care. Limited access to healthcare services and sexual education can contribute to a higher risk of Chlamydia infection.
One of the main factors contributing to the increased risk is the lack of affordable and accessible healthcare resources. Many individuals with low socioeconomic status may not have health insurance or the financial means to seek medical attention regularly. This can result in delayed diagnosis and treatment of Chlamydia, allowing the infection to progress and potentially cause more severe complications.
In addition to limited healthcare access, individuals with low socioeconomic status may also have limited access to sexual education. Comprehensive sexual education plays a crucial role in promoting safe sexual practices and raising awareness about sexually transmitted infections, including Chlamydia. Without proper education, individuals may lack the knowledge and understanding of how to protect themselves and their partners from Chlamydia transmission.
Low socioeconomic status often comes with other challenges that can increase the risk of Chlamydia. For example, individuals with limited financial resources may be more likely to engage in risky sexual behaviors as a result of seeking temporary escape or distraction. Substance abuse, such as alcohol or drugs, may be more prevalent in these communities, further increasing the chances of acquiring Chlamydia.
Addressing the higher risk of Chlamydia infection among individuals with low socioeconomic status requires a multi-faceted approach. It involves improving access to affordable healthcare services, including regular testing and treatment for Chlamydia. comprehensive sexual education programs should be implemented in schools and community centers to ensure that everyone, regardless of socioeconomic status, has access to accurate information about safe sex practices and STI prevention.
By addressing the barriers that individuals with low socioeconomic status face, we can work towards reducing the risk of Chlamydia transmission and creating a more equitable and inclusive healthcare system.
Conclusion
Understanding the risk factors associated with Chlamydia is crucial in promoting prevention strategies, promoting safe sexual practices, and raising awareness about the infection. By identifying and addressing these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their sexual partners from Chlamydia.
One effective way to prevent the transmission of Chlamydia is through education and awareness. Providing comprehensive sexual education that emphasizes the importance of safe sex practices, such as consistent and correct condom use, can help individuals make informed decisions about their sexual health.
In addition to education, promoting regular screenings and testing for Chlamydia can aid in early detection and treatment. Routine screenings can be an integral part of healthcare visits for sexually active individuals, allowing for timely diagnosis and appropriate intervention if necessary.
Creating a supportive environment that reduces stigmatization surrounding Chlamydia is also crucial. By normalizing discussions about sexual health and eliminating shame or embarrassment, individuals are more likely to seek the necessary medical care and support to address Chlamydia infection.
İmplementing prevention strategies, such as increasing access to affordable healthcare and sexual health services, can help reduce the risk of Chlamydia transmission. Individuals with limited resources or low socioeconomic status often face barriers in accessing healthcare and sexual education. By addressing these inequities, we can work towards reducing Chlamydia rates and improving overall sexual health outcomes.
Understanding the risk factors associated with Chlamydia is not only crucial for individual well-being but also for public health. By taking steps to address these risk factors, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of Chlamydia, promoting safe sexual practices, and ultimately improving the overall sexual health of our communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Example Question: How does unprotected sexual activity increase the risk of chlamydia?
Unprotected sexual activity, such as not using condoms, greatly increases the risk of contracting chlamydia. This is because chlamydia is primarily spread through sexual contact with an infected partner, and without the use of a barrier method, the bacteria can easily be transmitted.
Age And Chlamydia: Who is most at risk?
Young adults between the ages of 15 and 24 are the most at risk for chlamydia. This age group tends to have higher rates of sexual activity and may engage in riskier behaviors, such as having multiple partners or not using protection consistently.
Multiple Sexual Partners: Increasing the chlamydia risk?
Having multiple sexual partners increases the risk of chlamydia. Each new partner can potentially expose an individual to the bacteria, increasing the likelihood of infection. It is important to practice safe sex and get tested regularly if you have multiple partners.
Substance Abuse And Chlamydia: A Dangerous Combination
Substance abuse can increase the risk of chlamydia in several ways. People who are under the influence of drugs or alcohol may engage in risky sexual behaviors, such as unprotected sex or having multiple partners. substance abuse can impair judgment and decision-making, making individuals more likely to engage in high-risk sexual activity.
Lack Of Awareness And Education: Higher Chlamydia Risk
A lack of awareness and education about chlamydia puts individuals at a higher risk of infection. Without proper knowledge about the symptoms, transmission, and prevention of chlamydia, people may unknowingly engage in behaviors that increase their risk, such as not using protection or not getting tested regularly.
Reinfection And Chlamydia: Factors To Consider
Reinfection with chlamydia is possible and can occur if a person has sexual contact with an infected partner again after completing treatment. Factors that can increase the risk of reinfection include not completing the full course of antibiotics, having multiple partners, and engaging in unprotected sexual activity. It is important to take precautions and practice safe sex even after being treated for chlamydia.